Research
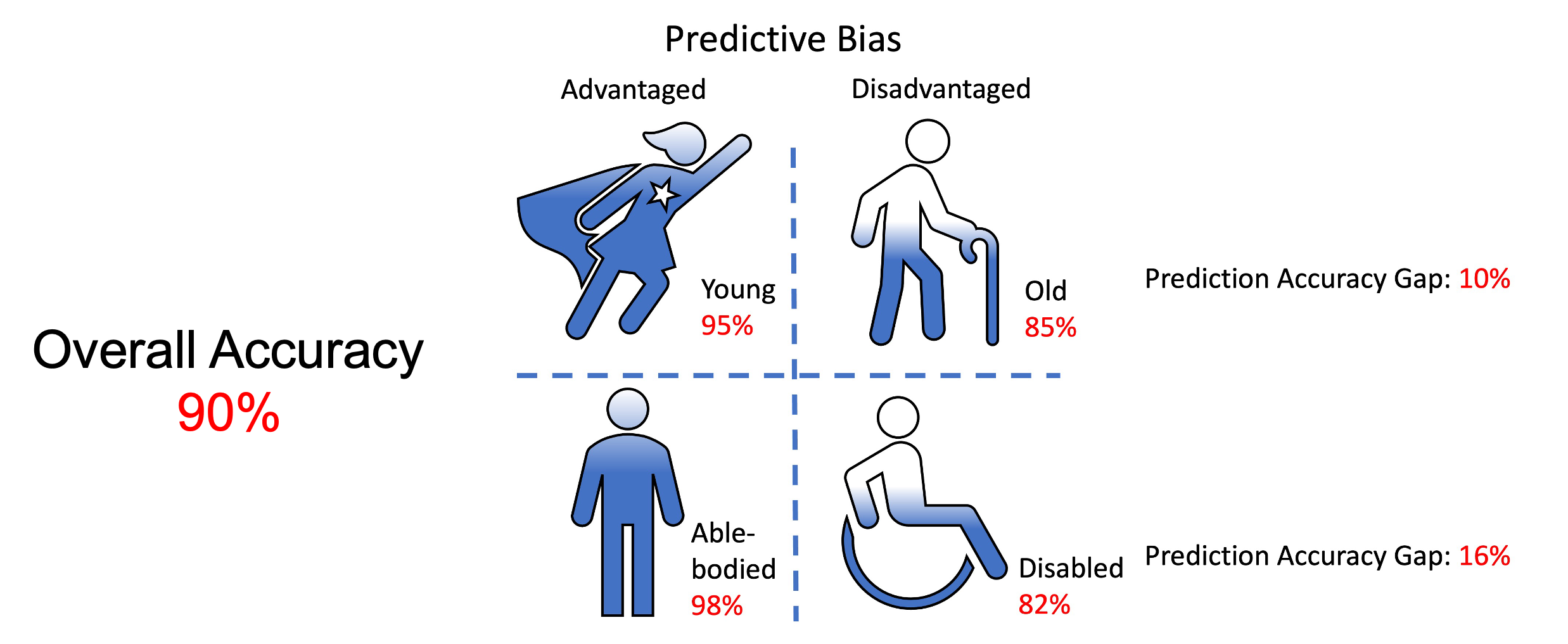 |
Despite superior predictive strength and explainability, we found that many AI-based travel demand models still face one major challenge—making worse predictions for disadvantaged population groups (e.g., racial and ethnic minorities, low-income individuals, and women) than the advantaged ones. Such discrepancy highlights inherent fairness issues within the models. |
A Fair AI Approach for Travel Demand Forecasting
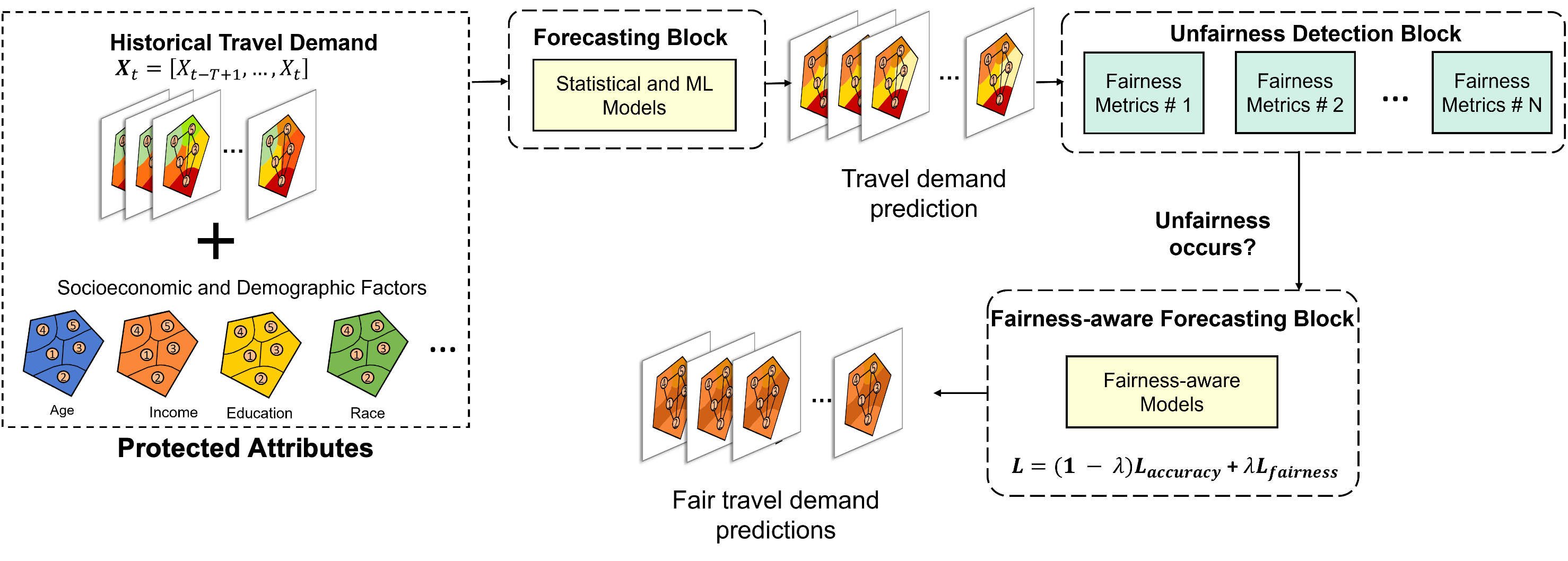 |
We designed a novel multiple correlation coefficient-based regularization method to address the algorithmic unfairness arising from MULTIPLE sensitive attributes (e.g., race, age, or sex) in AI-based travel demand models. Case studies using large-scale real-world ridehailing-trip data in Chicago, IL and Austin, TX showed that our solution can effectively preserve model's prediction accuracy while simultaneously enhancing fairness for multiple protected attributes. It is among the very first studies in travel demand modeling domain that addresses the algorithmic fairness issues |
[Link] Zhang, X., Ke, Q., & Zhao, X. (2024). Travel demand forecasting: A fair ai approach. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems.
Addressing Fairness Issues across Both Spatial and Temporal Domains Using Dynamic Weighting
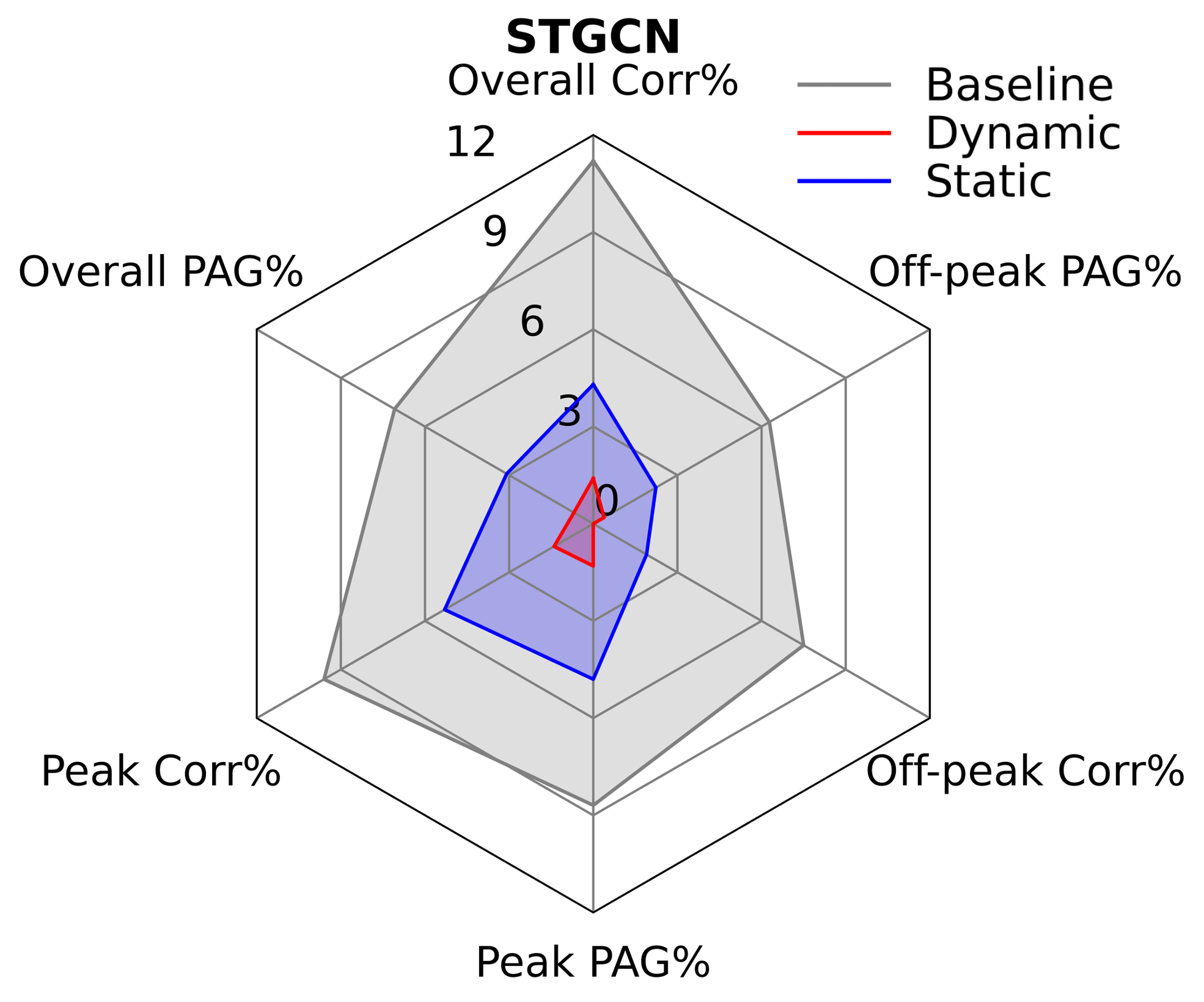 |
We further improved the fairness-enhancing framework by considering temporal prediction biases (e.g., higher prediction disparities in peak hours). We proposed a new regularization method called Fair Focal Loss (which is based on the well-known Focal Loss) and integrated dynamic weighting into the method. Specifically, Fair Focal Loss can dynamically learn and adjust the weights of different fairness losses based on the model's prediction fairness. This mechanism guides the model to focus on improving fairness where it is most needed and assigns less weight to predictions that have nearly or already achieved fairness. |
Zhang, X., & Zhao, X. (2024). Achieving fairness of spatiotemporal travel demand modeling with dynamic weighting. Will be presenting in TRB 2025.