Research
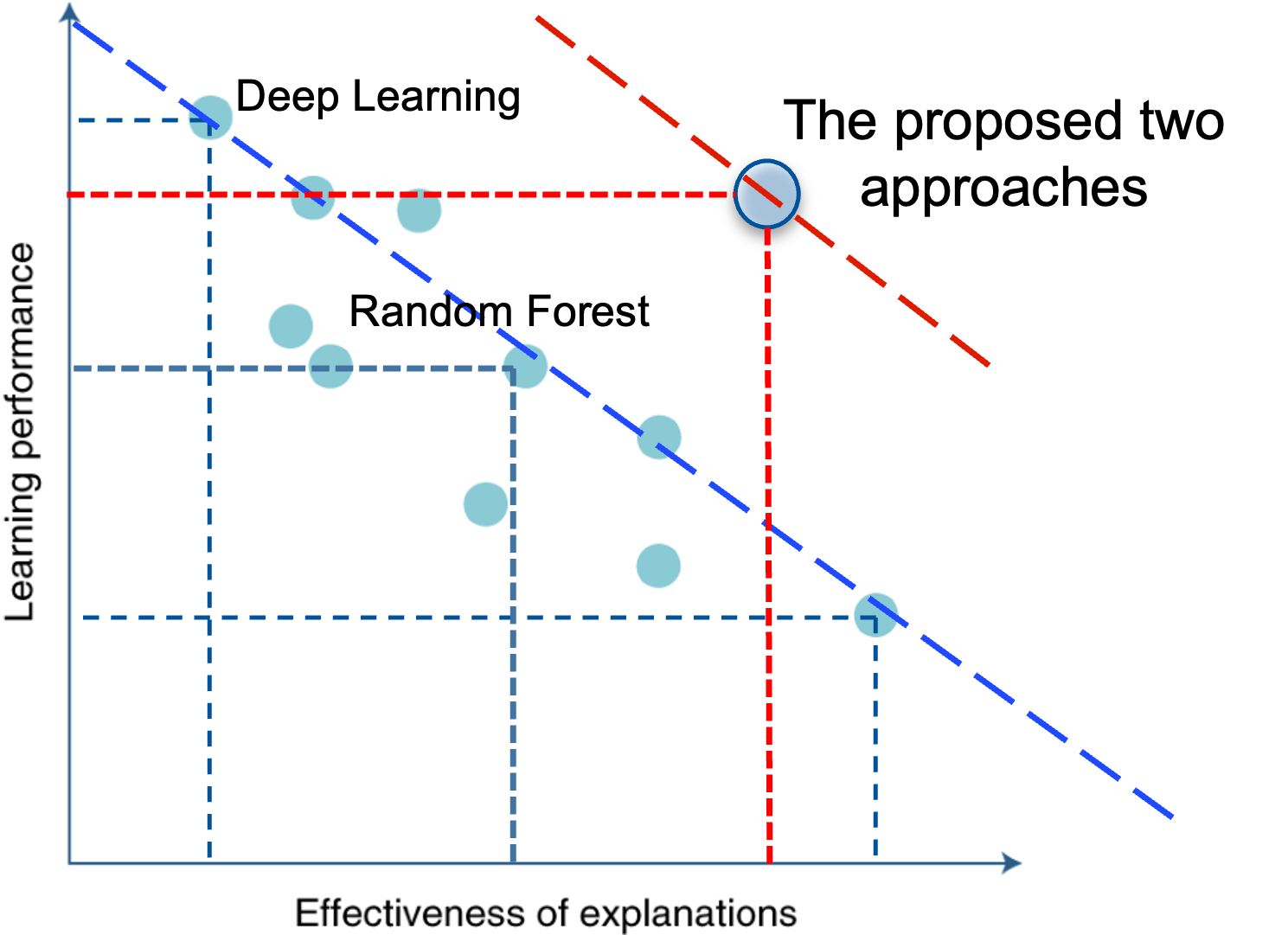 |
Besides achieving high accuracy, it is also crucial to understand which factors most significantly contribute to travel demand predictions and their relationships, as these behavioral insights can be used to develop effective transportation policies and interventions. However, there is a notable trade-off between machine learning model's prediction performance and interpretability. The model with higher prediction performance is usually less explainable, and the model with higher transparency (explainability) is often less accurate. Recognizing this, we have developed two novel AI-based travel demand forecasting methods that significantly enhance model explainability while maintaining prediction accuracy, pushing the trade-off between accuracy and model explainability to a new boundary. |
 |
Compositional Model: Clustering-aided Ensemble Method
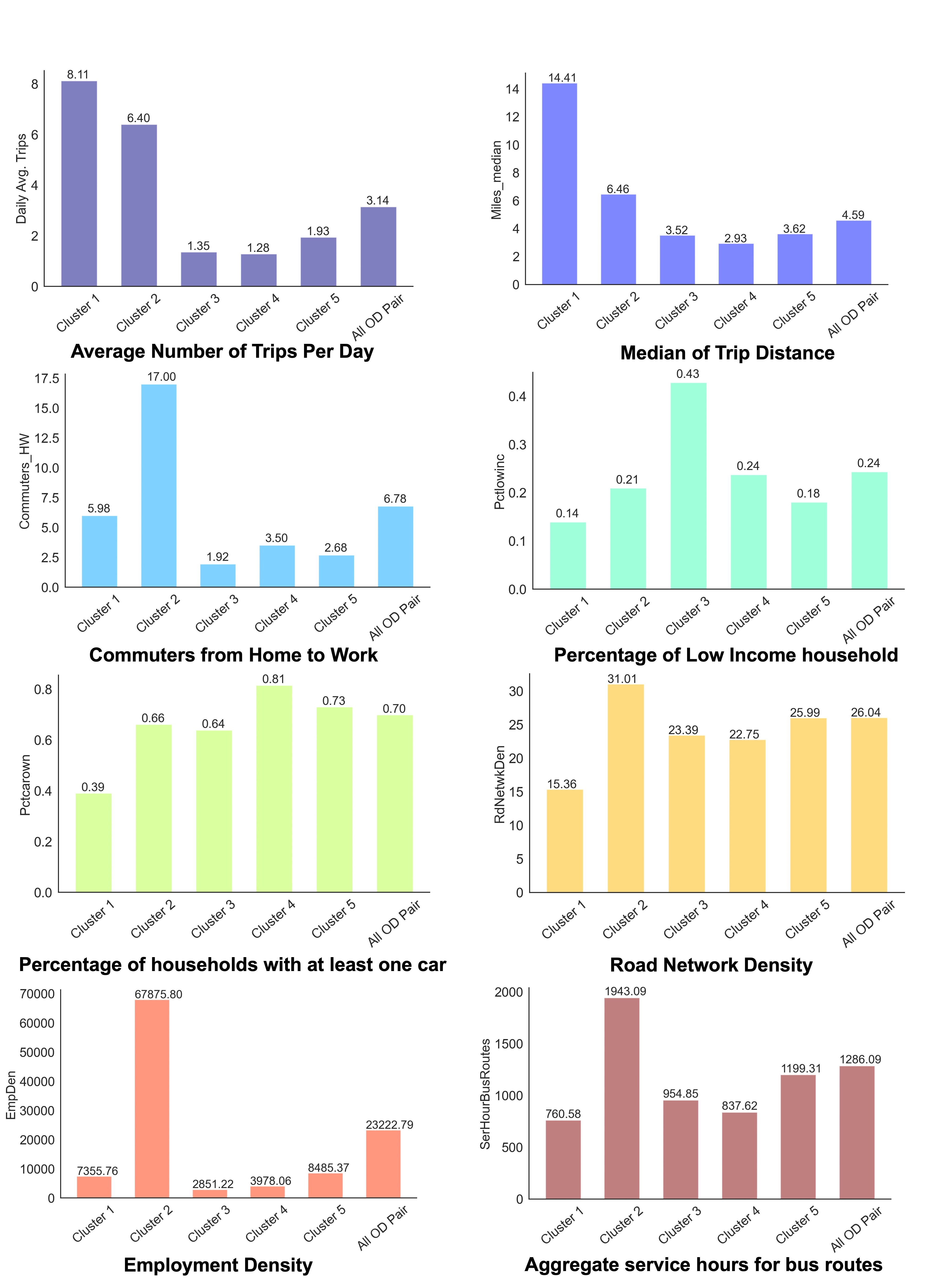 |
We proposed a GeoXAI (Geospatial Explainable AI) framework named Clustering-aided Ensemble Method (CEM) to forecast ridehailing services demand and identify key factors that shape ridehailing demand across space. We first applied K-Means to group the ridehailing-trip Origin-Destination (OD) Paris into five clusters based on their unique spatial characteristics. Then, we built cluster-specifc model, and use some explaination tools (such as variable importance) to interpret each cluster. Spatial heterogeneity was accounted for in the clustering process. |
[Link] Zhang, X., & Zhao, X. (2022). Machine learning approach for spatial modeling of ridesourcing demand. Journal of Transport Geography, 100(C).
Global Model
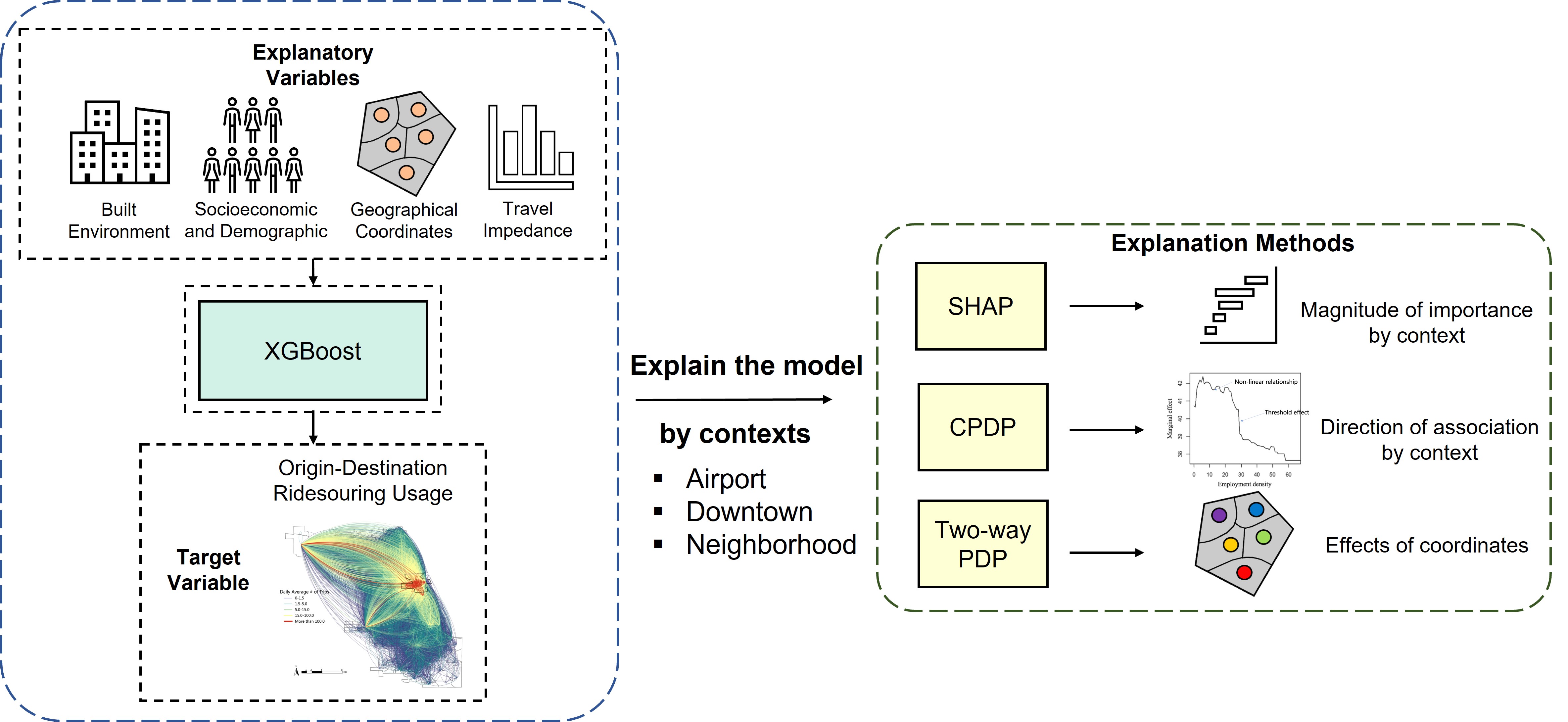 |
We proposed another GeoXAI framework as a complement to the compositional model to identify key factors that shape ridehailing demand across space by using only a global model. We captured the spatial heterogeneity by including the geographical coordinates of each observation as features into the machine learning model. Then, we explained the model's decision-making process across different locations by using two novel techniques: SHAP and Conditional Partial Dependence Plot (CPDP). |
[Link] Zhang, X., Zhou, Z., Xu, Y., & Zhao, X. (2024). Analyzing spatial heterogeneity of ridesourcing usage determinants using explainable machine learning. Journal of Transport Geography, 114, 103782.